Causes
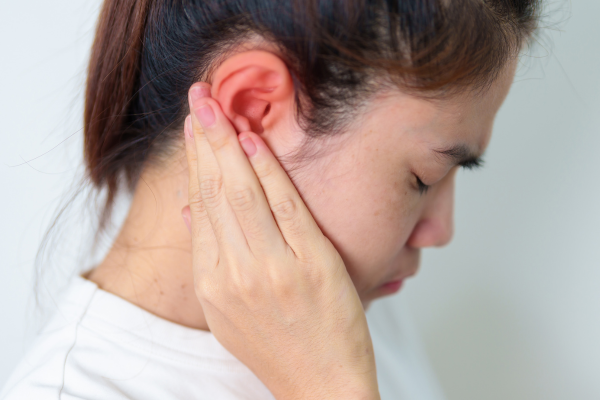
The cause of your swollen ear will depend on the part of your ear that is affected. The most common areas of your ear to experience swelling are the outer shell and your ear canal.
Auricular hematoma
Typically caused by blunt trauma or injury, an auricular hematoma is a collection of blood under the skin of your earlobe or outer ear. Not treating an auricular hematoma can lead to cauliflower ear – a deformity that affects many rugby players and boxers, for example.
Otitis externa
Otitis externa, also known as swimmer’s ear, is a common bacterial or fungal ear infection that can be caused by water that has been sitting in the ear canal for an extended period of time. It can lead to swelling, redness, and pain in the ears.
Cellulitis
A bacterial infection of the skin and tissues beneath the skin, causing redness, swelling, and tenderness in the affected area.
Allergic reaction
Allergic reactions can happen in response to an allergen, causing swelling, redness, and itchiness around the earlobe, outer ear, or inner ear structures.
The most common types of allergic reactions in ears include:
- Jewellery – a reaction to specific metals such as nickel.
- Insect bites – your ear may swell depending on the type of insect bite.
Abscess
A collection of pus within the ear tissue, typically caused by a bacterial infection, resulting in swelling, pain, and sometimes fever.
Piercings
Piercings can become swollen, red, and sore after they have been done but should go down after a few days with proper aftercare.